How To Access Raspberry Pi Remotely: The Ultimate Guide
Remote access to your Raspberry Pi has become an essential skill for hobbyists, developers, and professionals alike. Whether you're managing a home automation system, running a media server, or deploying IoT applications, knowing how to access Raspberry Pi remotely can save you time and increase productivity. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various methods, tools, and best practices to securely connect to your Raspberry Pi from anywhere in the world.
As technology advances, remote access to devices like Raspberry Pi has become more accessible than ever. This guide is designed to provide step-by-step instructions and expert advice to ensure your remote connection is both secure and efficient. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced user, this article will equip you with the knowledge you need.
Before diving into the technical details, it's important to understand the significance of secure remote access. Without proper security measures, your Raspberry Pi could become vulnerable to unauthorized access, which is why we'll also cover best practices for securing your connections. Let's get started!
Read also:Ryan Day Height And Weight A Comprehensive Guide To The Nfl Star
Why Remote Access Matters for Raspberry Pi
Remote access to Raspberry Pi offers numerous benefits, especially for users who manage servers, IoT devices, or home automation systems. Whether you're a developer working on a project or a hobbyist managing a personal setup, remote access allows you to control your Raspberry Pi without being physically present.
This section will explore:
- The importance of remote access in modern technology.
- Common scenarios where remote access is useful.
- Key considerations before setting up remote access.
Remote access not only enhances convenience but also improves efficiency by allowing you to troubleshoot issues, update software, or monitor system performance from anywhere. However, it's crucial to prioritize security to protect your device from potential threats.
Basic Requirements for Remote Access
Hardware and Software Setup
Before you can access your Raspberry Pi remotely, ensure that your device is properly set up with the necessary hardware and software. Below are the basic requirements:
- Raspberry Pi Model: Any model with networking capabilities (Raspberry Pi 3, 4, or later is recommended).
- Operating System: Raspbian OS (now known as Raspberry Pi OS) or any compatible Linux distribution.
- Network Connection: A stable internet connection via Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
- SSH Enabled: Secure Shell (SSH) must be enabled on your Raspberry Pi.
Having these prerequisites in place ensures a smooth setup process. Additionally, consider using a static IP address or dynamic DNS service to simplify remote access.
Understanding SSH for Remote Access
What is SSH?
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol used to securely access remote devices. It provides a secure channel over an unsecured network, ensuring that your data remains encrypted during transmission.
Read also:David Nehdar The Visionary Entrepreneur Revolutionizing The Business Landscape
Key features of SSH include:
- Encryption for data protection.
- Authentication to verify user identity.
- Support for file transfers and command execution.
SSH is one of the most reliable methods for accessing Raspberry Pi remotely. In the next section, we'll explore how to enable and configure SSH on your device.
Enabling SSH on Raspberry Pi
Enabling SSH on your Raspberry Pi is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to activate SSH:
- Boot your Raspberry Pi and log in to the operating system.
- Open the terminal and type the following command:
sudo raspi-config
3. Navigate to "Interfacing Options" and select "SSH." Enable SSH and exit the configuration tool.
Alternatively, you can enable SSH by placing an empty file named "ssh" in the boot partition of your Raspberry Pi SD card. This method is particularly useful if you don't have a monitor or keyboard connected to your device.
Using SSH Clients for Remote Access
Popular SSH Clients
Once SSH is enabled on your Raspberry Pi, you'll need an SSH client to establish a connection. Below are some of the most popular SSH clients:
- PuTTY: A widely used SSH client for Windows.
- Terminal: Built-in SSH client for macOS and Linux.
- Mobile Apps: SSH clients are available for Android and iOS devices, such as JuiceSSH and Serverauditor.
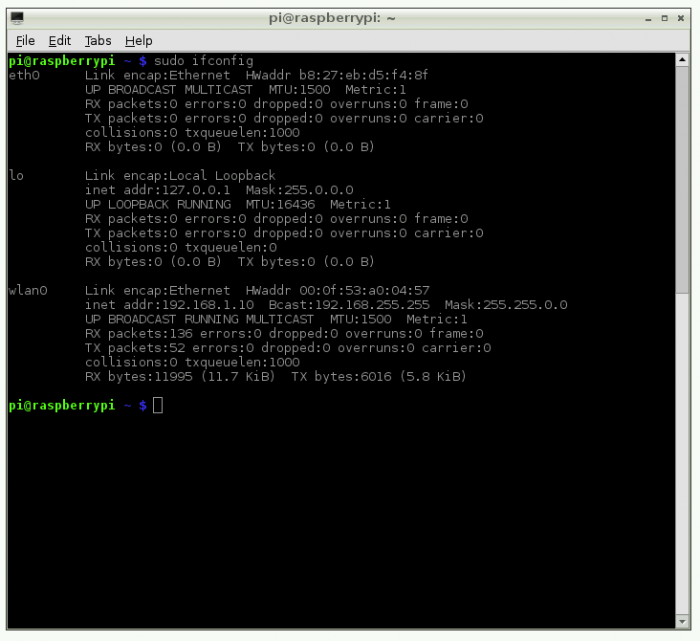
To connect using an SSH client, you'll need the IP address of your Raspberry Pi. Use the following command on your Raspberry Pi to find its IP address:
hostname -I
With the IP address, you can establish a secure connection using your preferred SSH client.
Setting Up Port Forwarding for Remote Access
What is Port Forwarding?
Port forwarding allows you to access your Raspberry Pi from outside your local network. It involves configuring your router to direct incoming traffic on a specific port to your Raspberry Pi's local IP address.
To set up port forwarding:
- Log in to your router's admin panel.
- Locate the port forwarding settings and create a new rule.
- Specify the port number (default SSH port is 22) and your Raspberry Pi's local IP address.
Once port forwarding is configured, you can connect to your Raspberry Pi using its public IP address. However, for added convenience, consider using a dynamic DNS service.
Dynamic DNS for Easy Remote Access
What is Dynamic DNS?
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) allows you to associate a domain name with your changing public IP address. This eliminates the need to remember or manually update your IP address whenever it changes.
Popular DDNS services include:
- No-IP
- DuckDNS
- FreeDNS
To set up DDNS:
- Create an account with a DDNS provider.
- Register a hostname and configure it to point to your public IP address.
- Install the DDNS client on your Raspberry Pi to keep the hostname updated.
With DDNS, you can access your Raspberry Pi using a memorable domain name instead of an IP address.
Securing Your Remote Connection
Best Practices for Security
Security is paramount when accessing Raspberry Pi remotely. Follow these best practices to protect your device:
- Use Strong Passwords: Avoid using default passwords and opt for strong, unique credentials.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Add an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification.
- Change Default SSH Port: Modify the default SSH port (22) to reduce the risk of automated attacks.
- Install a Firewall: Use tools like UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) to restrict access to specific ports and IP addresses.
Implementing these security measures ensures that your Raspberry Pi remains protected from unauthorized access.
Alternative Methods for Remote Access
Using VNC for Remote Desktop Access
While SSH is ideal for command-line access, VNC (Virtual Network Computing) allows you to remotely control the graphical user interface (GUI) of your Raspberry Pi. This is particularly useful for applications that require a visual interface.
To set up VNC:
- Install the VNC Server on your Raspberry Pi using the following command:
sudo apt install realvnc-vnc-server realvnc-vnc-viewer
2. Enable VNC by running sudo raspi-config and navigating to "Interfacing Options"> "VNC."
3. Connect to your Raspberry Pi using a VNC client on your computer or mobile device.
VNC provides a more interactive experience compared to SSH, making it suitable for tasks that require graphical interaction.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Solving Connection Problems
Despite careful setup, you may encounter issues when trying to access your Raspberry Pi remotely. Below are some common problems and their solutions:
- Connection Refused: Ensure SSH is enabled and the correct IP address is used.
- Timeout Errors: Check your network connection and verify port forwarding settings.
- Authentication Failed: Double-check your username and password, or ensure SSH keys are correctly configured.
If the issue persists, consult the logs on your Raspberry Pi for more information:
sudo journalctl -u ssh
Logging can help identify and resolve connection issues effectively.
Conclusion
Accessing Raspberry Pi remotely is a valuable skill that can enhance your productivity and flexibility in managing your projects. This ultimate guide has covered everything from basic requirements to advanced security measures, ensuring you have the tools and knowledge to set up a secure and efficient remote connection.
To recap, the key takeaways include:
- Enabling SSH and configuring SSH clients for command-line access.
- Setting up port forwarding and dynamic DNS for remote access outside your local network.
- Implementing security best practices to protect your Raspberry Pi from unauthorized access.
- Exploring alternative methods like VNC for graphical remote access.
We encourage you to share your experience or ask questions in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more tips and tutorials on Raspberry Pi and related technologies. Happy tinkering!
Table of Contents
- Why Remote Access Matters for Raspberry Pi
- Basic Requirements for Remote Access
- Understanding SSH for Remote Access
- Enabling SSH on Raspberry Pi
- Using SSH Clients for Remote Access
- Setting Up Port Forwarding for Remote Access
- Dynamic DNS for Easy Remote Access
- Securing Your Remote Connection
- Alternative Methods for Remote Access
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
Article Recommendations